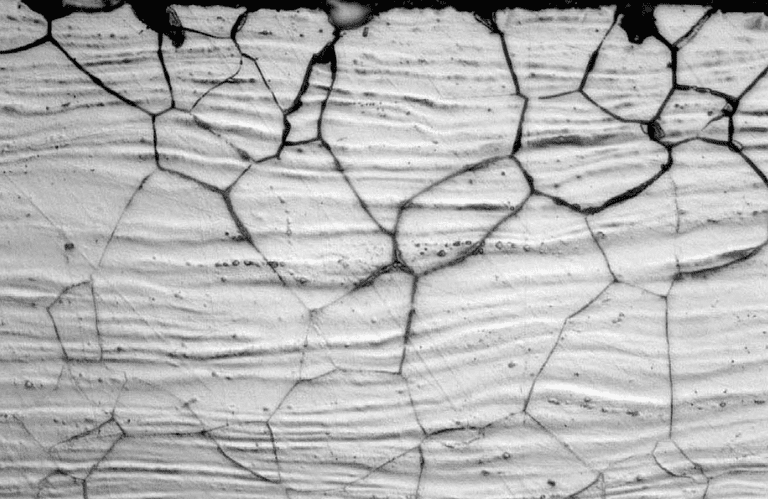
Metallography
SEM & EDX Analysis
By understanding why components fail, our clients can take appropriate measures to prevent similar instances in the future.
Explore how we work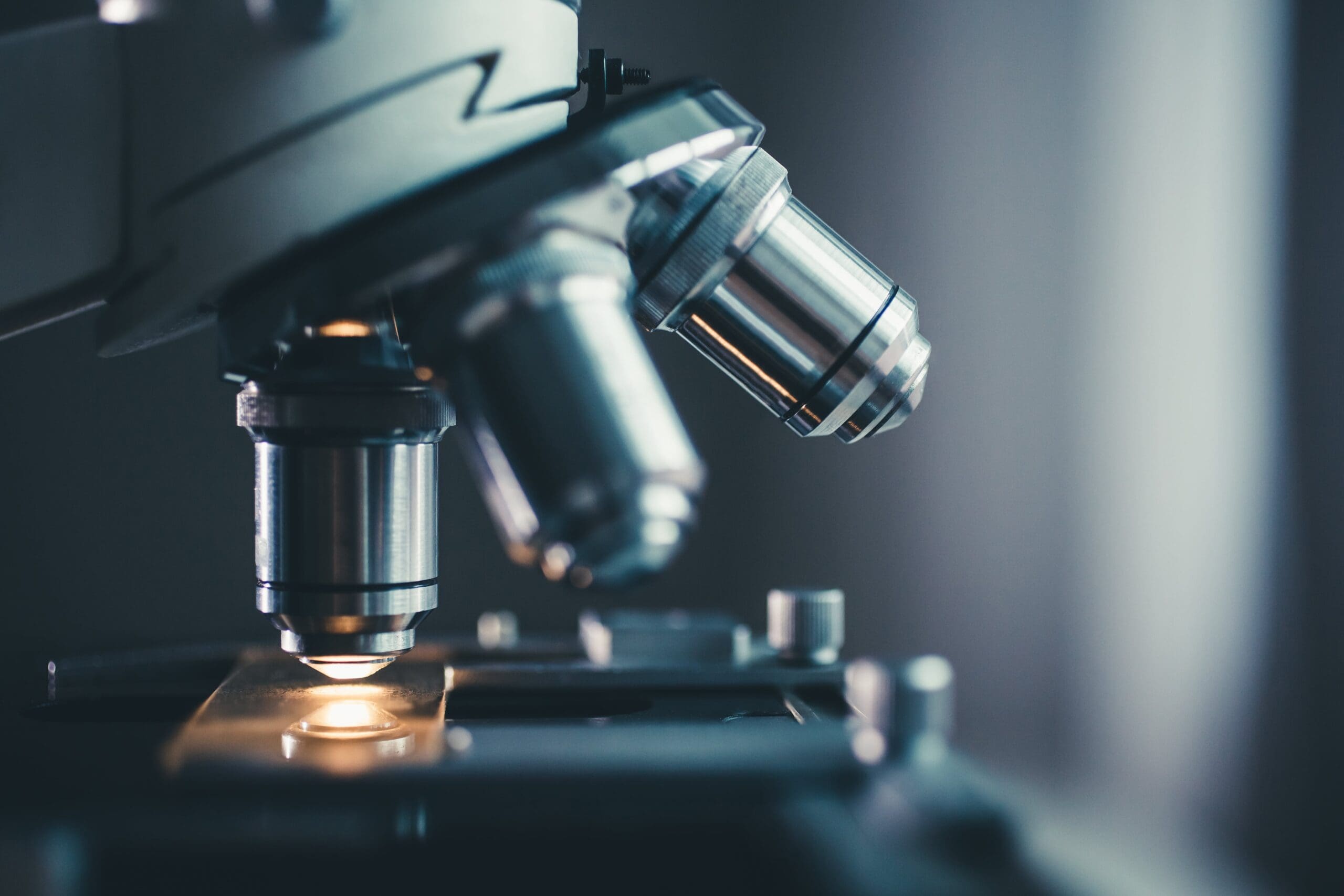
Interested? Let’s talk.
Send us an enquiry
What is SEM & EDX Analysis?
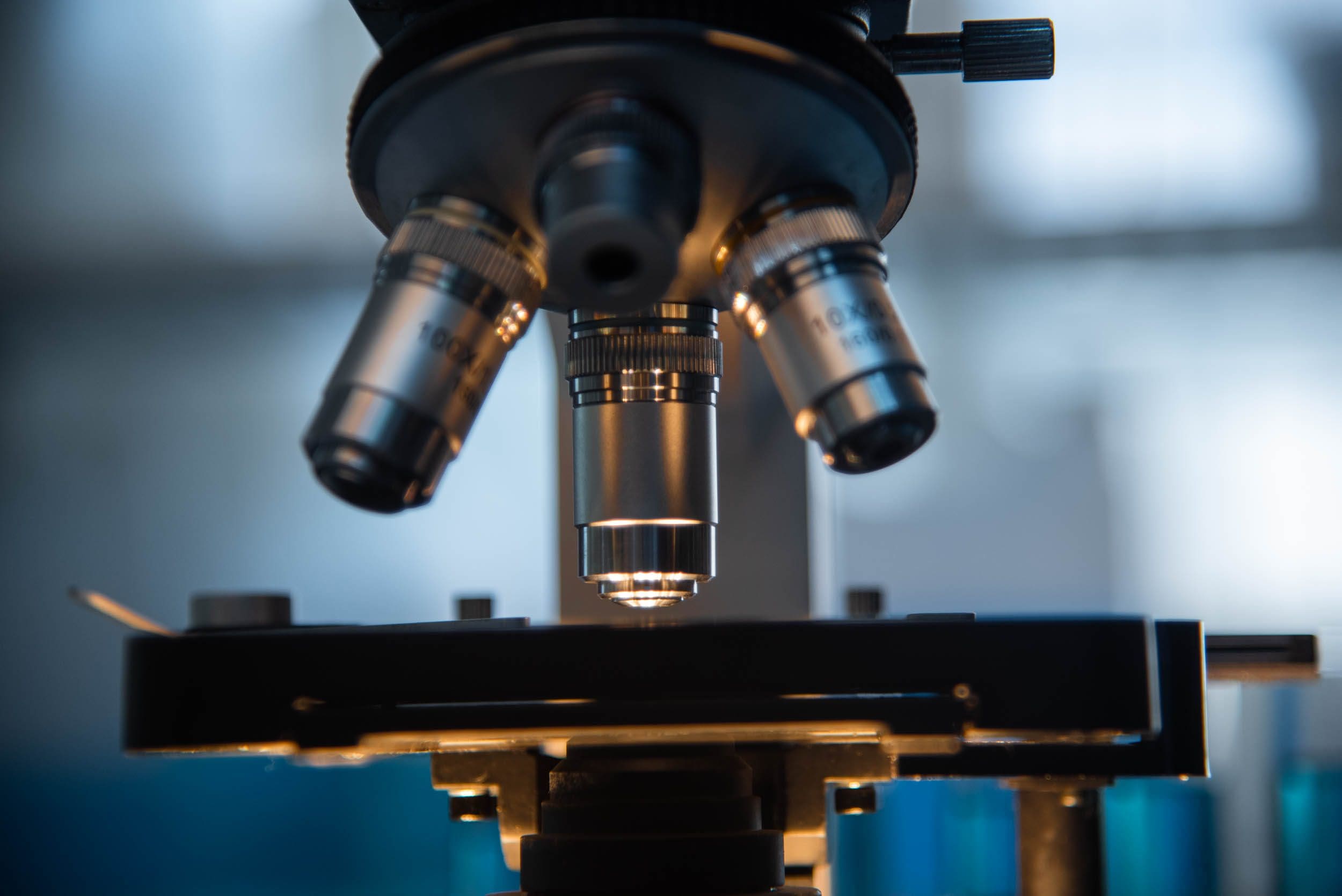
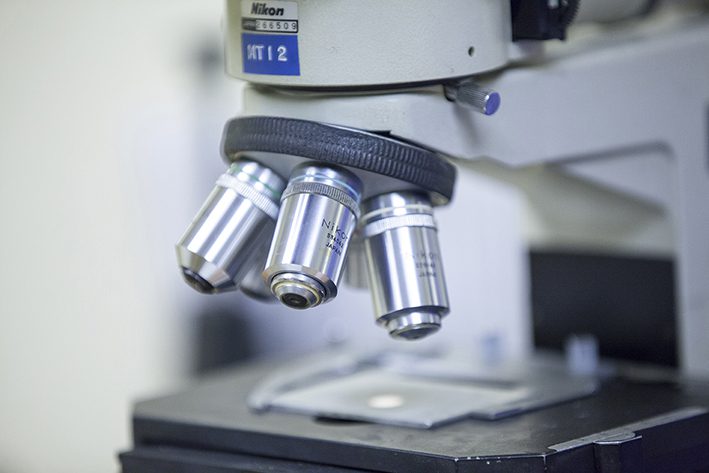
Scanning Electron Microscopy with Energy Dispersive X-ray Analysis (SEM-EDX) is a powerful analytical technique used for characterising the surface morphology, elemental composition, and chemical mapping of materials at a microscopic level. SEM is a widely used technique in metallurgy for analysing the microstructure and surface topography of samples. It is highly popular due to its ability to produce high-resolution images using a focused electron beam, scanning the surface of the sample at very high magnifications, ranging from 10 to 5,000 times.
At BES Group, we use SEM microscopy to detect cracks, contaminants, and fractures on the surface of materials to gain a deeper understanding of the behaviour and characteristics of samples at higher magnification levels compared to traditional microscopes. Knowing whether a material is prone to specific types of failure, like fatigue or stress corrosion cracking, or if there are any contaminants present on the surface, empowers our clients to make well-informed decisions regarding production processes. Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy (EDS or EDX) is another technique that we use in combination with SEM microscopy, for a comprehensive analysis of material composition.

Who we've partnered with





Key benefits of SEM & EDX Analysis
High Sensitivity
SEM-EDX analysis can detect even the smallest amounts of elements, making it ideal for analysing complex samples with low concentrations of certain particles.
Non-destructive
SEM-EDX analysis is a non-destructive test, so we can examine your samples without causing any damage to their structure or composition.
Wide Range of Samples
SEM-EDX analysis is extremely versatile, and can analyse various materials such as metals, polymers, ceramics, composites and much more.
Failure Analysis
SEM-EDX analysis offers in-depth information about the physical and structural characteristics of failed components, making it easier to identify why your product has failed.
Data-Driven Decision Making
The valuable insights gained from SEM-EDX analysis help in making informed decisions about production processes, improving quality control and efficiency, as well as minimising risks and reducing costs.
Enhanced Product Reliability
By addressing the underlying factors contributing to failures, SEM-EDX analysis plays a crucial role in improving product reliability, durability, and overall performance.
Let's talk about SEM & EDX Analysis
Send one of the team a message
Not seeing what you expected?
Try using our search
Explore what our clients say
Identifying failures with SEM & EDX Analysis
SEM or EDX analysis can be used for investigating the failure of components made from metal or other electrically conductive materials. Whether it’s copper pipework, fastener systems, high-tension wires, chains, cast housings, or even artificial hip implants, SEM/EDX analysis can provide crucial insights into the reasons behind a part’s failure.
It also helps them assess whether their choice of material is suitable for its intended application. Using x-rays emitted from the sample during the SEM process, EDS allows for a more detailed microanalysis of features observed on the scanning electron microscope.
The importance of identifying failures
By understanding how and why a part failed, manufacturers and consumers can take appropriate measures to prevent similar issues in the future, ultimately reducing costs and expenses.
Material failure investigations typically involve a range of tests, including visual examination, SEM (and EDX if necessary), metallography, chemical analysis, and mechanical testing (such as hardness, tensile, and impact testing).
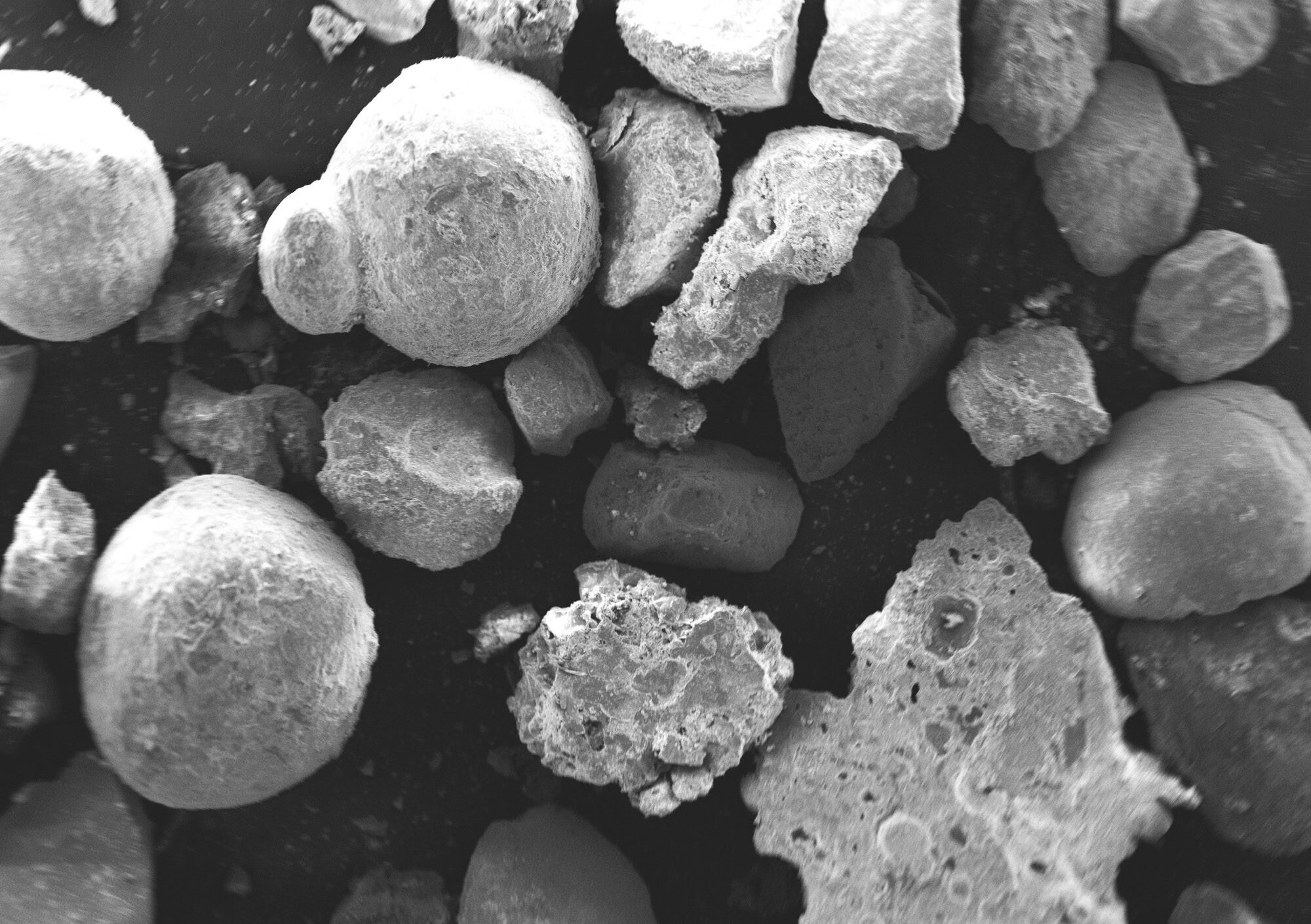
SEM & EDX Analysis from the BES Group
SEM analysis is a quick and cost-effective method for investigating metallurgical issues. It provides detailed and enlarged images of samples or materials without causing any significant damage. This technique is crucial in failure investigations as it allows for the analysis of the root cause of a failure at an elemental level. Additionally, it helps in identifying defects or flaws that cannot be observed through optical means alone.
SEM Analysis
SEM uses a focused electron beam to scan the surface of a specimen. As the electron beam interacts with the sample, various signals are emitted, including backscattered electrons, secondary electrons, and characteristic X-rays. These electrons provide valuable information about the composition and topography of the sample.
EDX Analysis
EDX is an analytical technique that detects characteristic X-rays emitted by the sample when it is bombarded with electrons. Each element in the sample emits X-rays at specific energies, allowing for the identification and quantification of elements present in the sample.


Let’s talk. Ask us anything.
Send one of the team a message
Why choose BES Group?

800+ expert engineers
Our team of skilled engineers possesses a wealth of expertise.
A legacy of 160+ years of experience
We’re always evolving our approach to future proof our services.

35,000 satisfied customers
A strong reputation for providing exceptional service.

An end-to-end solution
Servicing the full life cycle, from concept through to decommission.
Accredited assurance
Confidence assured with all relevant certifications and accreditations.
Frequently asked questions
How does SEM Analysis work?
Backscattered electrons are reflected back after interacting with the sample. They help us achieve high-resolution imaging of the elements present and detect differences in atomic number both on and below the surface of the material.
Secondary electrons originate from the atoms of the sample. They are produced when the electron beam excites the electrons within the sample, causing them to lose some energy in the process.
Key features:
- High-resolution imaging
- Surface morphology examination
- Microstructural analysis
- Fractography
How does EDX Analysis work?
The sample surface is bombarded with a high-energy electron beam, which leads to the absorption of energy by the electrons in the sample. As a result, inner shell electrons are ejected. The holes in the inner shells are then filled by electrons from higher energy levels, resulting in the emission of characteristic X-rays.
These emitted X-rays are measured for their energy and intensity by an energy-dispersive X-ray detector located near the sample. The detected X-rays are then sorted according to their energy, creating a spectrum that represents the elemental composition of the sample, and identifying the elements based on the characteristic X-ray peaks.
Key features:
- Elemental analysis
- Chemical mapping
- Particle analysis
- Surface contamination analysis
Sectors we service
Dive into the diverse landscapes where BES Group sparks innovation and drives impact.

Explore sector
Aerospace and Defence

Explore sector
Automotive

Explore sector
Consumer Products

Explore sector
Manufacturing

Explore sector
Marine and Offshore

Explore sector
Petrochemicals, Oil and Gas

Explore sector
Power and Utilities

Explore sector
Rail

Explore sector
Renewables

Explore sector
Retail


Let’s talk. Ask us anything.
Send one of the team a message
Insights & news
Browse our latest articles

A Guide to Young’s Modulus and Material Stiffness
Testing

A complete guide to Metal Failure Modes and Analysis
Testing

How combining NDT Methods ensures comprehensive asset protection
Testing

Factory Shutdowns: How to Manage Your Maintenance Operations Efficiently
Asset Reliability Electrical Inspection Testing

What Are the Different Methods of NDT Testing?
Testing
Other similar services...
Looking for something else? Explore similar services...
Let’s get you to the right person, fast.
Thank you, enquiry submitted!
Please check your inbox. We have sent you an email receipt of your enquiry.
We treat every enquiry with the upmost urgency. We’ll aim to get in touch with the relevant BES Group specialist and get back to you as soon as possible*.
Thank you again and have a great day.
 About BES Group
About BES Group Accreditations & Credentials
Accreditations & Credentials Our Environmental, Social & Governance
Our Environmental, Social & Governance Careers at BES Group
Careers at BES Group Our Senior Leadership Team
Our Senior Leadership Team






